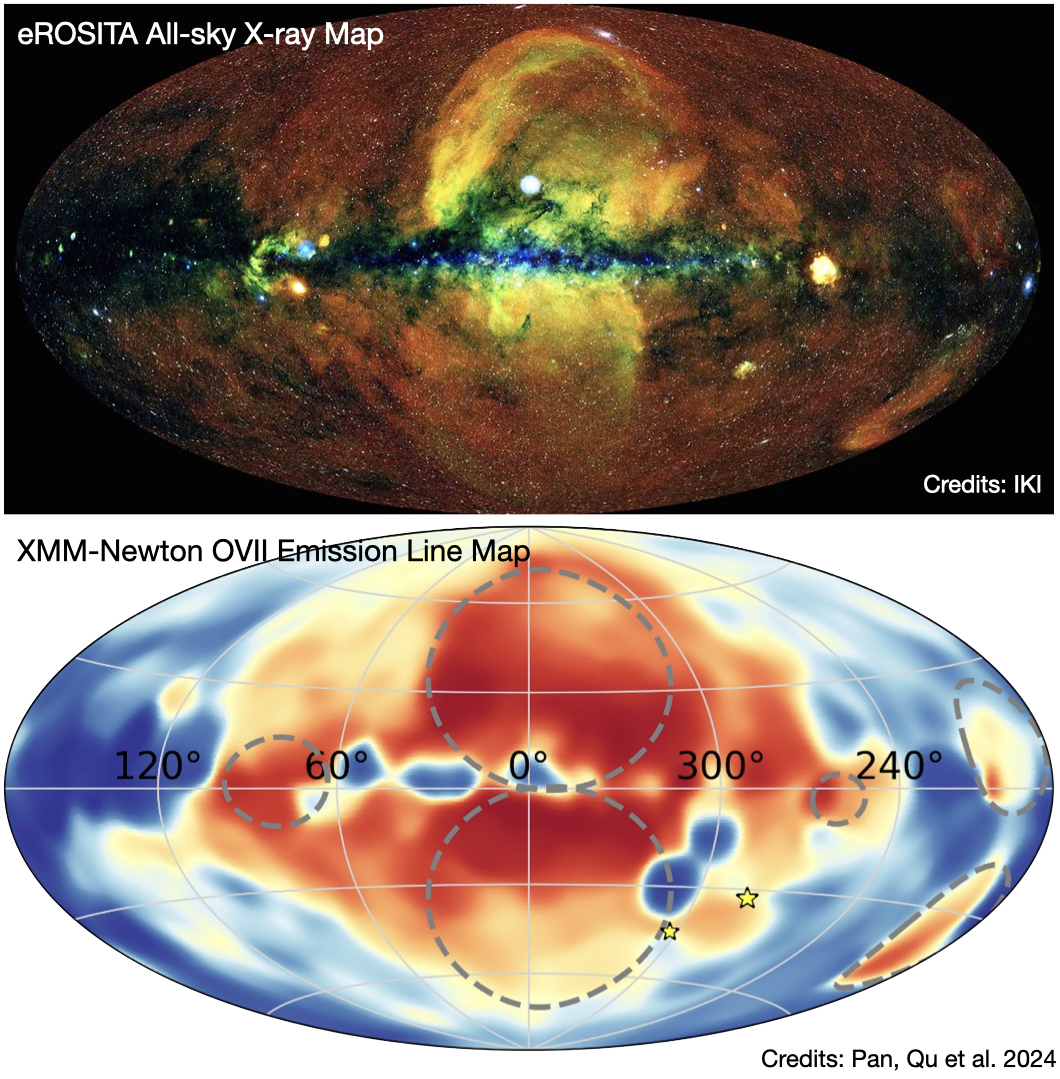
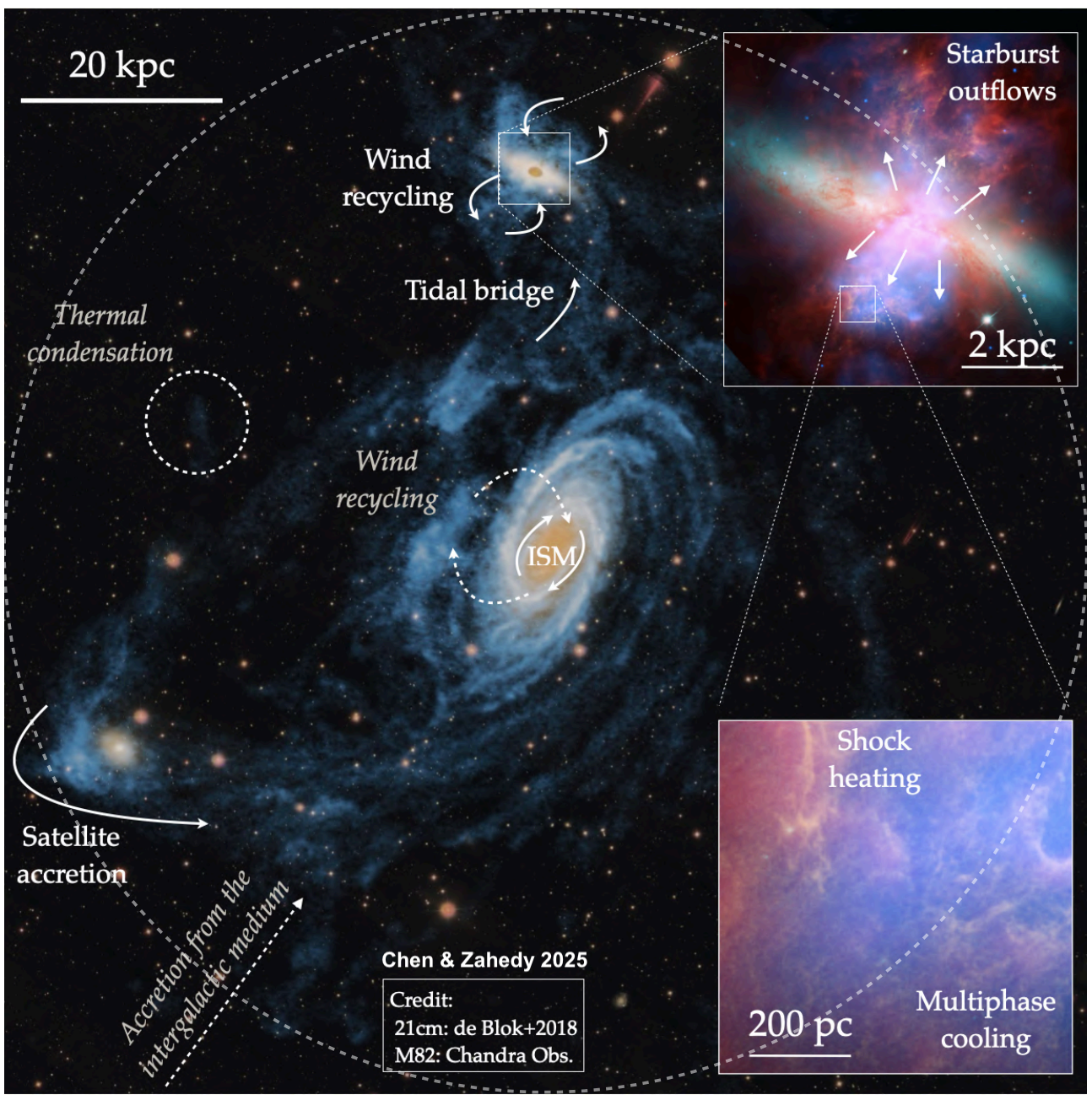
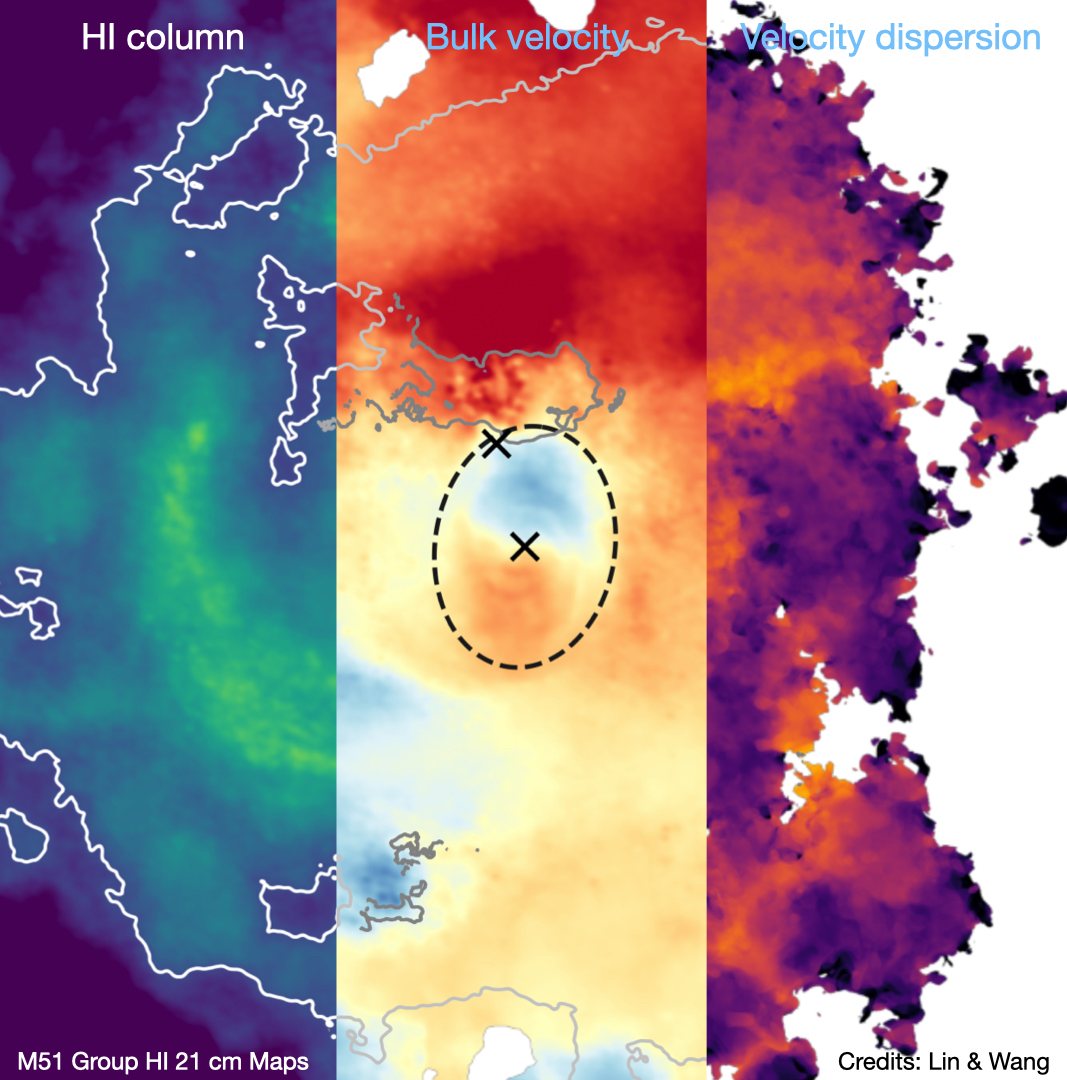
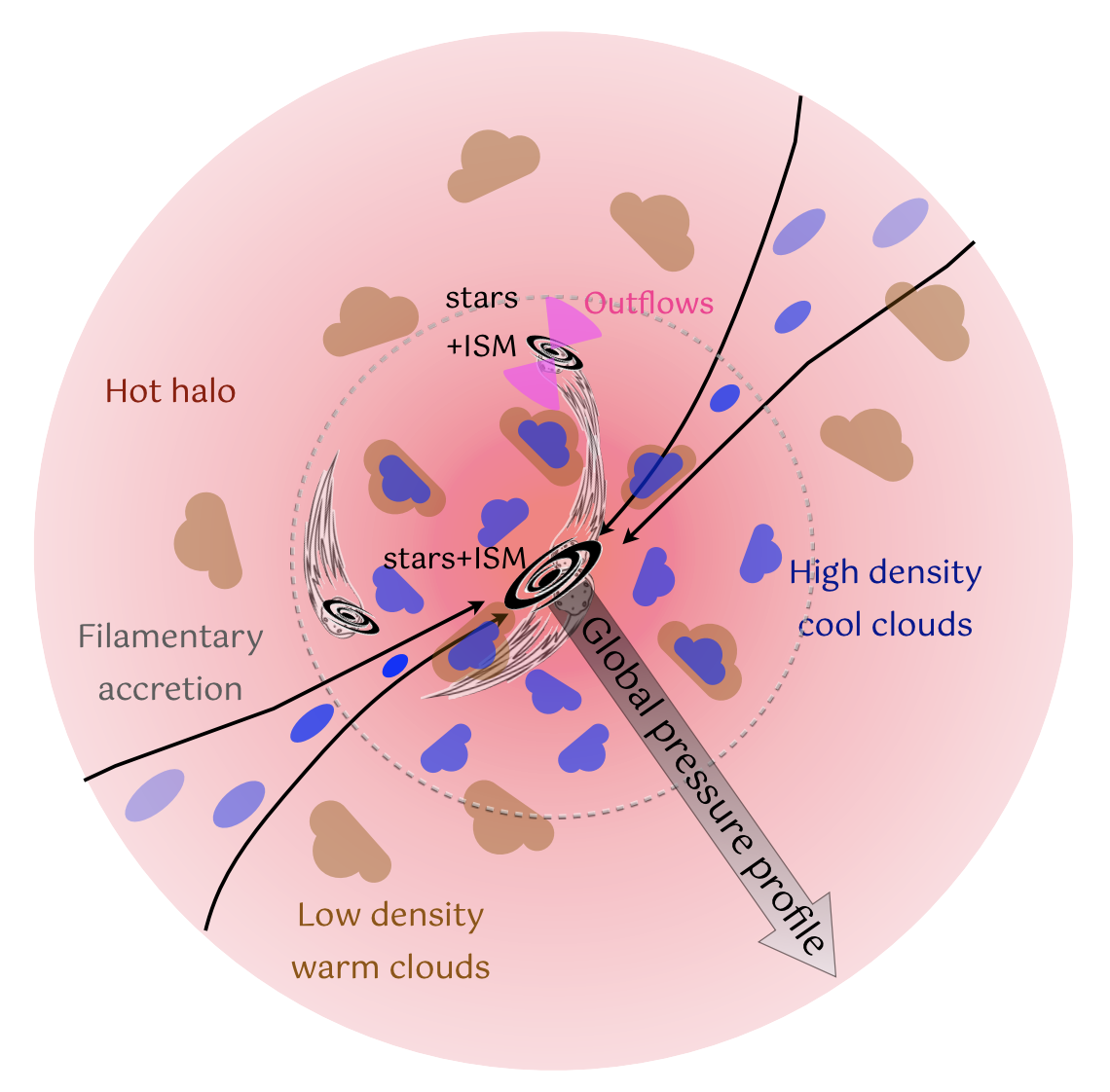
During galaxy formation and evolution, the gravitational energy released by the collapse of dark matter halos and the energy injected by feedback processes can significantly heat the CGM. (1) X-rays can be used to observe the hot gas in nearby galaxies. However, due to the limitations of current instruments, there is still considerable uncertainty in current research. The HUBS mission will greatly enhance X-ray observation capabilities. (2) The Sunyaev-Zel'dovich (SZ) effect, caused by the inverse Compton scattering of hot electrons on the Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB), can also be used to detect hot gas, complementing X-ray observations.
Upper panel: eROSITA all-sky X-ray map
Lower panel: Milky Way OVII emission map in XMM-Newton (Pan, Qu et al. 2024, X-LEAP I)